Featured 2
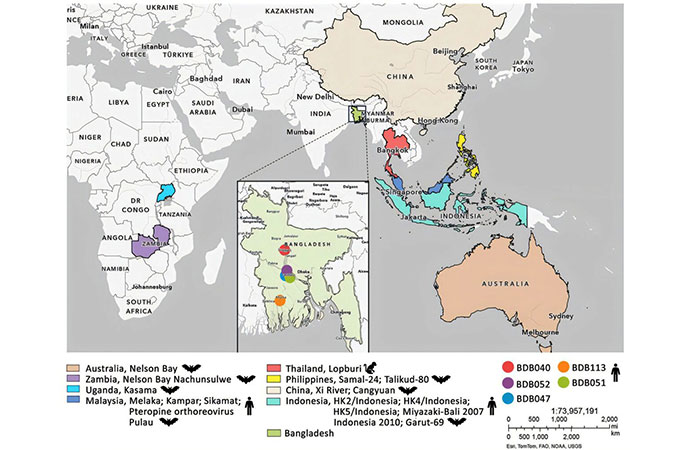
Study locations and locations for related viruses from study of bat reovirus as cause of acute respiratory disease and encephalitis in humans, Bangladesh, 2022–2023. Credit: Emerging Infectious Diseases (2026).
Infectious disease researchers have identified Pteropine orthoreoviruses (PRVs), a group of newly emergent bat-borne viruses, as the culprit for previously unexplained illness in five Bangladeshi patients, one of whom eventually died with unexplained illness.
The findings mark the first documented detection of bat-origin orthoreovirus-a kind of double-stranded RNA virus-in human cases of acute respiratory illness and encephalitis in Bangladesh. The study appears in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
All five patients had recently consumed raw date-palm sap-a treat also enjoyed by bats during winter months-and a known vector for Nipah infections in Bangladesh. Bats are the natural reservoir of numerous known and novel zoonotic viruses, including rabies, Nipah, Hendra, Marburg, and SARS1.
"Our findings highlight that the risk of zoonotic spillover associated with raw date palm sap consumption extends beyond Nipah virus," said Nischay Mishra, Ph.D., associate professor of epidemiology at the Center for Infection and Immunity, Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, and senior author of the study.
"He also underscores the importance of broad-spectrum surveillance programs to identify and mitigate public health risks from emerging bat-borne viruses."
Hospitalized between 2022 and 2023, the five patients had presumed Nipah infections but tested negative for Nipah virus despite having similar symptoms, including fever, vomiting, headache, fatigue, increased salivation, respiratory, and neurological complications.
In the new study, researchers performed high-throughput agnostic viral sequencing with CII's VirCapSeq-VERT system using biological samples taken from the five infected patients along with another 130-plus patients presenting with Nipah-like symptoms between 2006 and 2022, as part of a Nipah virus surveillance program established by the Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research (IEDCR), Bangladesh; International Center for Diarrheal Disease Research, Bangladesh (ICDDR,B); and U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Nischay and colleagues used VirCapSeq-VERT, a technology developed at the CII to quickly and efficiently screen for all viral infections of vertebrate origin. VirCapSeq-VERT is as sensitive as the gold-standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays while enabling simultaneous testing for thousands of viruses and providing near-complete genome sequences.
The study also confirmed the presence of the infectious virus by culturing the virus. All five patients experienced severe disease, although PRV infections reported elsewhere in neighboring countries have often been milder, suggesting that less severe cases in Bangladesh may be underrecognized.
"A new addition of zoonotic spillover causes respiratory and neurological complications following consumption of raw date palm sap next to Nipah virus infection," says Tahmina Shirin, Ph.D., Director, Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control, and Research (IEDCR), as well as the National Influenza Center (NIC) in Bangladesh.
In a study conducted more recently, Mishra and colleagues identified the source of infections by identifying genetically similar Pteropine orthoreoviruses in bats captured in proximity to the five human cases near the Padma River Basin (unpublished data).
"This [research] provides critical evidence linking bat reservoirs to human infection. We are now working to understand the spillover mechanisms from bats to humans and domestic animals, as well as the broader ecology of emerging bat-borne viruses in communities along the Padma River Basin," says Ariful Islam, bat-borne disease ecologist and epidemiologist at Charles Sturt University, Australia, and co-first author of the study.
Previously, Mishra and colleagues used the technology to identify a viral threat to transplant patients, neurologic manifestations in an infant with COVID-19, enterovirus infection as a cause for a rare neurological condition, and the origins of chikungunya in Brazil. Not only approved for experimental use, VirCapSeq-VERT has also obtained regulatory approval for clinical use.
The study's co-first author is Sharmin Sultana, assistant professor of Virology and Senior Scientific Officer at the Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research (IEDCR) in Bangladesh.
From Medical Xpress























Leave a Comment
Recent Posts
The Scramble for Energy
The severe turmoil in global energy markets promises not to spare anyo ...
Enhancing the Capacity of Elec ...
The Bangladesh Academy for Rural Development (BARD), Cumilla, in partn ...
Saleh Shibly quietly performing as PM’s press secret ..
PTA negotiations feature in Dhaka-Jakarta discussion ..
Dhaka decides to strengthen cultural diplomacy, boos ..
Chinese Vice Foreign Minister Sun Weidong to visit B ..